Google Analiytc Review
Google Analytics is a powerful tool used by businesses and website owners to track and analyze website traffic and user behavior. It provides valuable insights into how people find and use your website, which pages they visit most, how long they stay, and much more. By setting up goals and tracking conversions, you can understand the effectiveness of your marketing efforts and make data-driven decisions to optimize your site.
Reviews of Google Analytics often highlight its comprehensive features, user-friendly interface, and the ability to generate detailed reports. However, some users may find it overwhelming initially due to the wealth of data it offers. Overall, it’s considered an essential tool for businesses aiming to understand their online audience and improve their online presence.
Is Google Analytics any good?
Absolutely! Google Analytics is widely regarded as one of the best web analytics tools available. Here are some reasons why it’s considered excellent:
- Comprehensive Data: It provides a vast array of data about website visitors, their behavior, and interactions on your site. This data includes demographics, location, device used, pages visited, time spent on pages, and more.
- Free Version: For most users, the standard version of Google Analytics is free, making it accessible to small businesses and individuals.
- User-Friendly Interface: Despite the complexity of the data it provides, the interface is intuitive and user-friendly. It allows both beginners and experts to navigate and gather insights.
- Customization and Reporting: It allows for customization of reports and dashboards, enabling users to focus on specific metrics or KPIs that matter most to their business.
- Integration: It integrates well with other Google tools like Google Ads, Search Console, and Data Studio, providing a more comprehensive view of your online presence and marketing efforts.
- Insights for Optimization: With the data it provides, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their websites, improve user experience, and enhance marketing strategies.
While Google Analytics is highly praised, some users may find it overwhelming due to the sheer amount of data and features available. Additionally, ensuring correct setup and interpretation of the data can be challenging for beginners.
Overall, Google Analytics is considered an invaluable tool for understanding website performance and user behavior, aiding businesses in making data-driven decisions to improve their online presence.
How do I review Google Analytics data?
Reviewing Google Analytics data involves several steps to access and interpret the information effectively. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Access Google Analytics:
- Sign In: Go to Google Analytics (analytics.google.com) and sign in using your Google account.
- Select the Property: If you have multiple websites or apps tracked, select the relevant property/view you want to review.
2. Navigate the Interface:
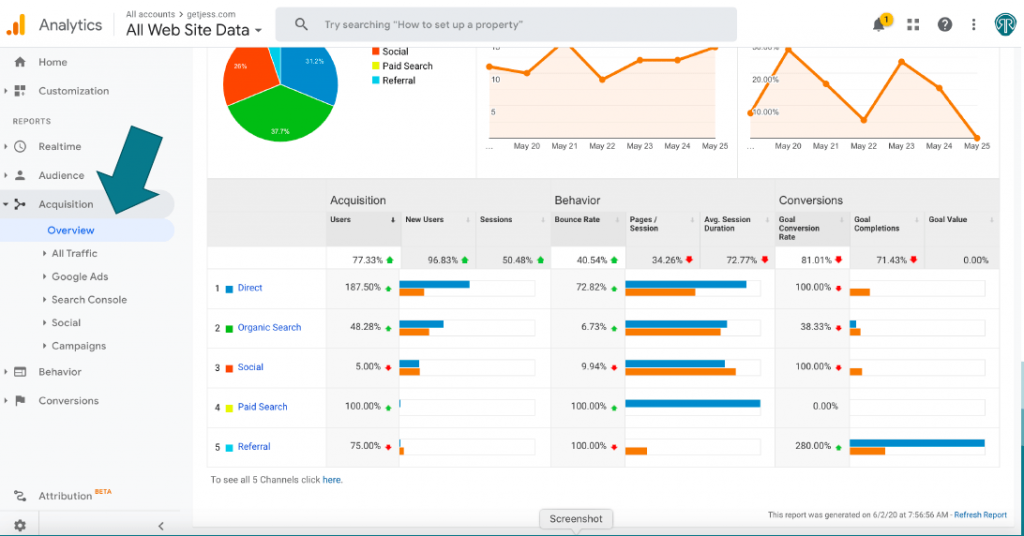
- Dashboard Overview: The default view presents an overview of key metrics. Explore various sections like Audience, Acquisition, Behavior, and Conversions.
- Audience Overview: Understand who visits your site (demographics, location, device, etc.).
- Acquisition Overview: Learn where your traffic comes from (organic search, direct, referrals, social, etc.).
- Behavior Overview: See what visitors do on your site (popular pages, time spent, bounce rate, etc.).
- Conversion Overview: If set up, track specific goals or conversions (purchases, sign-ups, etc.).
3. Analyze Specific Reports:
- Custom Reports: Create custom reports tailored to your specific needs.
- Time Frame: Analyze data over different time frames to identify trends or patterns.
- Segmentation: Use segments to filter data for more detailed analysis (new users, organic traffic, etc.).
4. Set Goals and Funnels (if applicable):
- Goals: Define specific actions you want users to take (form submissions, purchases, etc.).
- Funnels: For e-commerce or multi-step processes, set up funnels to track user progression.
5. Interpret the Data:
- Compare Metrics: Compare different metrics to identify correlations or discrepancies.
- Identify Trends: Look for patterns over time and seasonal variations.
- Draw Conclusions: Use the data to draw insights about user behavior and site performance.
6. Take Action:
- Optimization: Use insights gained to optimize content, marketing strategies, or user experience.
- Experimentation: Test changes based on data insights and measure their impact.
7. Learn & Iterate:
- Continual Review: Regularly check analytics to monitor changes and assess the effectiveness of implemented strategies.
- Learning Resources: Utilize Google Analytics Academy or other resources to deepen your understanding.
Remember, Google Analytics offers a wealth of data, so focusing on the metrics that align with your business goals is crucial. Experimentation and iteration based on insights gathered are key to leveraging the full potential of the tool.
Is Google Analytics course worth it?
Taking a Google Analytics course can be immensely valuable, especially if you’re looking to deepen your understanding of the platform or want to use it more effectively for your business. Here are a few reasons why a course might be worth it:
- In-depth Knowledge: Courses provide structured learning, ensuring you cover various aspects of Google Analytics comprehensively. They often cover advanced features, best practices, and real-world applications that might not be immediately apparent when self-learning.
- Hands-on Experience: Many courses offer practical exercises, case studies, and projects that allow you to apply what you learn in real scenarios. This hands-on experience can solidify your understanding of how to use Google Analytics effectively.
- Certification: Some courses offer certification upon completion. While certification might not be mandatory, it can add credibility to your skill set and might be beneficial professionally, especially in certain job roles.
- Expert Guidance: Courses are often led by experienced instructors who can clarify complex concepts, answer questions, and provide guidance based on their practical experience.
- Updated Information: Google Analytics evolves, and courses usually keep pace with updates and changes in the platform, ensuring you learn the latest features and functionalities.
However, whether a course is worth it depends on your specific needs, prior knowledge, and learning preferences. If you’re already comfortable with the basics and use Google Analytics regularly, you might find free online resources, tutorials, and documentation sufficient to expand your knowledge.
Consider factors like the course content, cost, reviews from previous learners, and your learning style before investing in a course. Google Analytics Academy offers free courses and resources directly from Google, which can be a great starting point.
Ultimately, a course can be worth it if it helps you gain a deeper understanding of Google Analytics, empowers you to utilize its features effectively, and aligns with your professional or business goals.
Is Google Analytics still accurate?
Google Analytics remains a reliable and widely used web analytics platform. Its accuracy depends on various factors:
- Data Collection Setup: Accurate implementation of the tracking code and configurations is crucial. If set up correctly, it provides reliable data.
- Data Sampling: In some cases, especially with high-traffic websites, Google Analytics might use sampled data for certain reports. While this doesn’t significantly impact overall accuracy, it’s essential to be aware of when analyzing specific data sets.
- Ad Blockers and Privacy Settings: Some users employ ad blockers or have privacy settings that might limit the data captured by Google Analytics. This can affect the accuracy of the data, particularly in tracking certain user behaviors.
- Bot Filtering: Google Analytics has mechanisms to filter out bot traffic, but some bots might still get counted, impacting accuracy.
- Cross-device Tracking: It might be challenging to track users across multiple devices accurately, which could affect data accuracy, especially in understanding the complete user journey.
- Platform Updates: Google periodically updates and improves Analytics to enhance accuracy and functionality.
While Google Analytics provides valuable insights, it’s essential to complement its data with other sources and tools for a more comprehensive understanding of user behavior and website performance. Comparing data from different analytics platforms or sources can help verify trends and patterns.
Overall, Google Analytics remains a highly reliable tool for understanding website traffic and user behavior, but it’s essential to be aware of its limitations and constantly monitor for potential discrepancies.
What is better than Google Analytics?
Several analytics tools offer features that might complement or enhance aspects of what Google Analytics provides. The “better” option often depends on specific needs, preferences, and the depth of analysis required. Here are a few alternatives that some users find valuable:
- Adobe Analytics: Offers enterprise-level analytics with robust features for large businesses. It focuses on deep data analysis, real-time tracking, and personalized customer experiences.
- Matomo (formerly Piwik): A free and open-source alternative to Google Analytics, allowing greater control over data privacy and storage. It’s customizable and can be self-hosted.
- Mixpanel: Focuses on user-based analytics, offering insights into individual user behavior across various interactions. It’s well-suited for analyzing user journeys and product analytics.
- Heap Analytics: Automates data collection without the need for event tracking setups, making it easier to retroactively analyze user interactions.
- Kissmetrics: Emphasizes customer behavior analytics and customer journey tracking, providing insights for optimizing conversion funnels.
- Crazy Egg: Primarily focuses on visual analytics using heatmaps, scrollmaps, and user session recordings to understand user behavior.
Each of these tools has its strengths, and their suitability depends on factors like the size of the business, specific analytics requirements, data privacy concerns, and budget. Many businesses find that using a combination of tools or integrating multiple analytics platforms provides a more holistic view of their online presence and user behavior.
While these alternatives offer unique features, Google Analytics remains a popular choice due to its robustness, integrations, and the fact that the standard version is free for most users, making it accessible and comprehensive for many businesses.
Is Google Analytics worth it for beginners?
Absolutely! Google Analytics is a valuable tool for beginners as it provides a comprehensive understanding of website traffic and user behavior. Here’s why it’s worth it:
- Free Access: The standard version of Google Analytics is free for most users, making it an accessible option for beginners who want to understand their website’s performance without a significant financial investment.
- User-Friendly Interface: While it can seem overwhelming at first, Google Analytics offers an intuitive interface that beginners can navigate with ease. The default reports provide valuable insights, and there are plenty of tutorials available to help newcomers get started.
- Learning Opportunities: Using Google Analytics as a beginner can be a great learning experience. It introduces fundamental concepts of web analytics, including understanding metrics, user behavior, traffic sources, and conversions.
- Foundational Knowledge: Learning to use Google Analytics early in your journey as a website owner or marketer sets a solid foundation for understanding data-driven decision-making. It’s a skill that becomes increasingly valuable as you progress.
- Resource Availability: There is a wealth of online resources, tutorials, courses, and community forums dedicated to Google Analytics. Beginners can easily find guidance and support when learning to use the platform.
- Business Insights: Even for beginners, Google Analytics can offer valuable insights into user demographics, popular content, traffic sources, and more. These insights can inform content strategies and marketing efforts.
While it might take some time to become comfortable navigating the platform and understanding the various metrics, Google Analytics is a fantastic starting point for beginners looking to understand and optimize their website’s performance. As you become more adept, you can explore its advanced features and functionalities.
Are Google Analytics free?
Yes, Google Analytics offers a free version for most users. The standard version of Google Analytics is available at no cost and provides robust features for analyzing website traffic and user behavior.
The free version includes a wide range of functionalities, such as:
- Basic Reporting: Access to standard reports like audience demographics, acquisition channels, behavior flow, and more.
- Real-Time Data: Monitor live user activity on your website.
- Customization: Create custom reports, segments, and goals to track specific metrics aligned with your business objectives.
- Integrations: Connect with other Google products like Google Ads, Search Console, and Data Studio for more comprehensive insights.
- Mobile App Tracking: Track app usage and performance for mobile applications.
For most small to medium-sized businesses, the free version of Google Analytics is sufficient to gather crucial insights into website performance, user behavior, and traffic sources.
However, there is an enterprise-level version called Google Analytics 360 that caters to larger enterprises with more advanced needs. Google Analytics 360 offers additional features, enhanced data limits, dedicated support, and customization options, but it comes with a substantial cost.
For beginners or those managing smaller websites, the free version of Google Analytics is a powerful tool that provides valuable insights without requiring any monetary investment.
How much Google Analytics cost?
Google Analytics offers two main versions: the standard version, which is free for most users, and Google Analytics 360, an enterprise-level solution with advanced features that comes with a cost.
- Google Analytics Standard (Free): This version is available at no cost for most users. It includes a wide range of features for tracking website traffic, user behavior, conversions, and more. Small to medium-sized businesses often find the standard version sufficient for their analytics needs.
- Google Analytics 360 (Paid): Google Analytics 360 is the premium, enterprise-level version of Google Analytics. It offers additional capabilities, such as increased data limits, advanced integrations, dedicated support, unsampled reports, and more customization options. However, the pricing for Google Analytics 360 varies based on factors like website traffic volume and specific business requirements. It typically involves a significant subscription fee, which can range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars per month, depending on the level of usage and services needed.
The cost of Google Analytics 360 is tailored to individual businesses, and Google doesn’t provide a standardized pricing model publicly. Organizations interested in Google Analytics 360 typically need to contact Google or authorized resellers directly to discuss pricing based on their specific needs and usage.
For most users, especially smaller businesses, the standard version of Google Analytics, which is free, is a robust and comprehensive analytics tool that fulfills their requirements. Only larger enterprises with more extensive data needs and specific demands opt for the Google Analytics 360 premium solution.
Do I need Google Analytics?
The need for Google Analytics depends on your specific goals, website, and how crucial data-driven insights are to your operations. Here are some scenarios where using Google Analytics could be beneficial:
- Understanding Website Traffic: If you own a website or manage an online presence, Google Analytics helps understand who visits your site, where they come from, which pages they visit, and how they interact with your content.
- Measuring Performance: It provides valuable data about the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns, user engagement, conversion rates, and the overall performance of your website.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: If you rely on data to make informed decisions about your website’s content, design, marketing strategies, or user experience improvements, Google Analytics is invaluable.
- E-commerce and Conversions: For e-commerce sites or businesses focused on conversions (sign-ups, purchases, etc.), Google Analytics helps track and optimize these crucial metrics.
- Targeted Marketing: Understanding your audience demographics, interests, and behaviors helps tailor marketing strategies and content to better suit your visitors.
- Optimizing User Experience: Analyzing user behavior on your site can highlight areas that need improvement, guiding you in optimizing the user experience.
Ultimately, whether you need Google Analytics depends on your objectives and the level of detail you require regarding your website’s performance and user behavior. For many businesses and website owners, especially those seeking to grow and optimize their online presence, Google Analytics offers valuable insights that contribute to informed decision-making and better performance.
Can I make money with Google Analytics?
Directly making money through Google Analytics itself isn’t typical, as it’s primarily a tool for analyzing website traffic and user behavior rather than a platform for generating revenue. However, Google Analytics can indirectly contribute to making money in several ways:
- Optimizing Marketing Campaigns: By analyzing data in Google Analytics, you can identify which marketing channels or campaigns drive the most traffic or conversions. Optimizing your marketing strategies based on this data can lead to increased sales or conversions, thereby generating revenue.
- Improving Website Performance: Understanding user behavior through Google Analytics helps in optimizing your website. A better user experience can lead to higher engagement, increased time spent on site, and potentially more conversions, positively impacting revenue.
- Enhancing Ad Revenue: If you monetize your website through ads, understanding your audience and their behavior can help optimize ad placement and content. This can increase ad engagement and revenue generated from ad networks like Google AdSense.
- Client Services: If you offer website or marketing services to clients, leveraging your expertise in Google Analytics to provide data-driven insights and recommendations can be a valuable service, generating income through consulting or analytics services.
- Educational Content: Creating educational content, courses, or resources related to Google Analytics and selling them to businesses or individuals seeking to enhance their analytics knowledge can be a source of income.
While Google Analytics itself doesn’t directly make money, leveraging the insights gained from its data can lead to more informed decisions that positively impact revenue streams, marketing efforts, and business performance. Additionally, expertise in using Google Analytics can create opportunities for consulting, teaching, or providing services to others seeking assistance in leveraging data analytics for their businesses.
Is Google Analytics outdated?
Google Analytics remained a widely used and relevant tool for website analytics. However, the landscape of digital analytics is constantly evolving, and newer tools and approaches continue to emerge.
Google has been introducing updates and improvements to Google Analytics, aiming to enhance its capabilities and adapt to changing user needs and privacy concerns. For instance, they introduced Google Analytics 4 (GA4), an updated version focused on machine learning, cross-device tracking, and privacy-centric features to align with evolving data regulations.
While Google Analytics remains a powerful tool, some users might consider it in need of updates in certain areas, especially regarding:
- Privacy Concerns: With increasing emphasis on user privacy and data protection regulations (like GDPR and CCPA), there’s a growing need for analytics tools to adapt their tracking methods. Google Analytics has been adjusting its features to accommodate these changes.
- Data Sampling: In some cases, Google Analytics might use sampled data for large datasets, potentially impacting the granularity of reports and analyses.
- Cross-Device Tracking: Tracking users across different devices for a cohesive understanding of the user journey continues to be a challenge due to privacy restrictions and technological limitations.
- Real-Time Analytics: While Google Analytics provides real-time data, some users might seek more immediate or granular real-time insights.
To address these concerns and adapt to the changing landscape, Google periodically updates its analytics tools. However, some users might prefer or explore alternative analytics platforms that offer different features, better privacy controls, or more tailored solutions to their specific needs.
In summary, while Google Analytics remains a powerful and widely used tool, users should keep an eye on updates and developments to ensure they are leveraging the latest features and functionalities that align with their evolving requirements.

What Google Analytics Cannot do?
Google Analytics is a robust tool for understanding website traffic and user behavior, but it does have limitations and areas where it may not provide comprehensive insights. Here are some things Google Analytics cannot do or areas where it might have limitations:
- Individual User Identification: Google Analytics doesn’t reveal the identity of individual users due to privacy policies. It provides aggregated data on user behavior but doesn’t track or display personally identifiable information.
- Tracking Offline Interactions: It primarily focuses on online interactions and might not seamlessly integrate data from offline sources, such as in-store purchases, phone calls, or traditional marketing efforts.
- Real-Time Accuracy: While Google Analytics provides real-time data, it might not capture every single interaction immediately. Some data might be delayed or subject to sampling, especially with high-traffic websites.
- Cross-Device Tracking: Tracking users across multiple devices accurately can be challenging due to privacy restrictions and limitations in cookie-based tracking methods.
- Attribution Modeling Complexity: While it offers attribution modeling, determining the exact influence of each touchpoint in a user’s journey, especially in complex conversion paths, can be intricate and might not provide a complete picture.
- Granular Data for Small Sample Sizes: In some cases, when dealing with small sample sizes, data might be aggregated or sampled, which could limit the granularity of insights.
- Data Accuracy with Ad Blockers: Users employing ad blockers or privacy tools may limit the data collected by Google Analytics, potentially impacting the accuracy of tracked information.
- Predictive Analytics: While Google Analytics offers some machine learning-driven insights, it might not provide advanced predictive analytics capabilities available in specialized predictive modeling tools.
- Direct Revenue Tracking for All Scenarios: Tracking revenue directly, especially in complex scenarios such as offline conversions or multi-channel attribution, might require additional setups or integrations beyond standard configurations.
- Custom Data Integration Complexity: Integrating custom or non-standard data sources might require additional setup and configurations, and might not always seamlessly integrate with Google Analytics.
Understanding these limitations can help users make informed decisions about leveraging Google Analytics and exploring additional tools or methods to address specific needs that might fall beyond its scope.

When should I use Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is valuable in various scenarios and stages of website development or business operations. Here are some key instances when using Google Analytics is particularly beneficial:
- Website Launch: Implement Google Analytics when launching a new website to track its performance from the start. It helps gather data on user behavior, traffic sources, and content performance.
- Marketing Campaigns: Use Google Analytics to measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. It provides insights into which channels drive the most traffic or conversions, allowing you to optimize marketing strategies.
- Content Optimization: Analyze user behavior to understand which content resonates most with your audience. This helps in creating and optimizing content to improve engagement and conversions.
- Conversion Tracking: Set up goals and track conversions to monitor specific actions users take on your site, such as purchases, sign-ups, or downloads. This helps in evaluating the success of your website’s objectives.
- User Experience Improvement: Use data from Google Analytics to identify areas where users face challenges or drop off. Optimizing the user experience based on these insights can enhance engagement and retention.
- E-commerce Optimization: For online stores, Google Analytics helps track sales, analyze product performance, and understand customer behavior throughout the purchasing process.
- Audience Insights: Understand your website visitors better by analyzing demographic data, location, devices used, and interests. This information helps tailor your content and marketing efforts.
- Periodic Performance Evaluation: Continuously use Google Analytics to monitor website performance, track trends over time, and identify areas for improvement.
In essence, Google Analytics is beneficial throughout the lifecycle of a website or online business. It’s instrumental in providing insights to improve user experience, optimize marketing efforts, understand audience behavior, and make data-driven decisions to achieve business goals. Utilizing Google Analytics regularly ensures a data-driven approach to website management and marketing strategies.
What has replaced Google Analytics?
Google Analytics remained a widely used and prominent tool in the field of web analytics. While it continues to be a go-to solution for many businesses, several emerging tools and platforms have gained popularity or offer alternatives in specific areas:
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4): Google introduced GA4 as an updated version aiming to address modern analytics needs, including enhanced machine learning capabilities, cross-device tracking, and privacy-centric features. GA4 is positioned as the next generation of Google Analytics, offering more advanced insights and adaptability.
- Privacy-Centric Analytics Tools: With increasing concerns about user privacy and data regulations, several analytics tools have emerged focusing on enhanced privacy features and compliance with regulations. Some of these tools prioritize user consent management and offer more transparent data collection methods.
- Specialized Analytics Platforms: Various analytics platforms specialize in specific areas or offer advanced features that might complement or expand on Google Analytics’ capabilities. These platforms focus on aspects like user behavior analysis, heatmaps, session recordings, or advanced segmentation and attribution modeling.
- Self-Hosted and Open-Source Solutions: Some businesses opt for self-hosted or open-source analytics solutions like Matomo (formerly Piwik) due to greater control over data and privacy. These solutions offer customizable analytics tracking and are often self-hosted, providing more control over data storage and usage.
- Enterprise-Level Solutions: For larger enterprises with extensive data needs and sophisticated analytics requirements, there are enterprise-level analytics platforms that offer robust features, advanced integrations, and dedicated support tailored to complex business structures.
While Google Analytics maintains its position as a widely used and versatile tool, the evolving landscape of digital analytics and the increasing focus on privacy and data compliance have led to the emergence of alternative tools and specialized platforms. Many businesses might choose to complement Google Analytics with other tools or explore newer options to meet specific analytics needs or address evolving privacy concerns.
What is the strongest competitor to Google Analytics?
Several analytics tools compete with Google Analytics, offering varying features and strengths that cater to different user needs. Identifying a single strongest competitor depends on specific requirements and priorities. Here are a few prominent competitors:
- Adobe Analytics: Often considered one of the strongest competitors to Google Analytics, especially in the enterprise space. Adobe Analytics offers robust features for deep data analysis, real-time tracking, and personalized customer experiences.
- Matomo (formerly Piwik): A notable open-source alternative that provides extensive customization options, privacy control, and self-hosting capabilities. It’s favored by those seeking more control over data and analytics tracking.
- Mixpanel: Focused on user-based analytics, Mixpanel provides insights into individual user behavior across various interactions. It’s highly effective for analyzing user journeys and product analytics.
- Heap Analytics: Differentiates itself by automatically capturing user interactions without the need for predefined event tracking setups. This simplifies data collection and retroactive analysis of user interactions.
- Crazy Egg: Specializes in visual analytics, offering heatmaps, scrollmaps, and user session recordings to understand user behavior visually. It’s often used for optimizing website layouts and user experience.
- Kissmetrics: Concentrates on customer behavior analytics and tracking the customer journey, providing insights valuable for optimizing conversion funnels.
Each of these competitors has its strengths and might be considered the strongest depending on specific business requirements, such as the need for customization, depth of analysis, user-based tracking, visualization, or privacy concerns.
While these tools compete with Google Analytics, it’s essential to assess which one aligns best with your specific goals, budget, and the depth of analytics required for your business or website. Many users continue to use Google Analytics alongside or in combination with other analytics tools to leverage the strengths of multiple platforms.
What is a competitor to Google Analytics?
There are several competitors to Google Analytics that offer similar functionalities for tracking website traffic, user behavior, and providing insights. Here are some notable alternatives:
- Adobe Analytics: Positioned as a strong competitor to Google Analytics, especially in the enterprise space. It offers robust features for deep data analysis, real-time tracking, and personalized customer experiences.
- Matomo (formerly Piwik): An open-source alternative that allows extensive customization, privacy control, and self-hosting capabilities. It’s favored by those seeking more control over data and analytics tracking.
- Mixpanel: Focuses on user-based analytics, providing insights into individual user behavior across various interactions. It’s highly effective for analyzing user journeys and product analytics.
- Heap Analytics: Differentiates itself by automatically capturing user interactions without the need for predefined event tracking setups. This simplifies data collection and retroactive analysis of user interactions.
- Crazy Egg: Specializes in visual analytics, offering heatmaps, scrollmaps, and user session recordings to understand user behavior visually. It’s often used for optimizing website layouts and user experience.
- Kissmetrics: Concentrates on customer behavior analytics and tracking the customer journey, providing insights valuable for optimizing conversion funnels.
Each of these competitors offers its unique features and strengths, appealing to different user preferences and business requirements. They aim to provide analytics solutions that suit various needs, from basic website traffic tracking to more advanced user behavior analysis.
Choosing the right competitor to Google Analytics often depends on factors such as the depth of analysis required, specific functionalities needed, budget, data privacy concerns, and the level of customization desired for tracking and analyzing website or app performance.

Why is Google Analytics so difficult?
Google Analytics can initially appear challenging due to several reasons:
- Complexity of Data: It collects a vast amount of data about website visitors, user behavior, and traffic sources. Understanding which metrics to focus on and how to interpret this data can be overwhelming for beginners.
- Abundance of Features: Google Analytics offers numerous features and customization options, which can make the interface seem complex. Navigating through different reports, settings, and configurations might be daunting initially.
- Learning Curve: For those new to web analytics, terms like bounce rate, sessions, segments, and goals might be unfamiliar. Learning the terminology and concepts of analytics can take time.
- Technical Setup: Implementing the tracking code correctly and setting up goals or custom configurations might require technical knowledge or website development skills.
- Interpretation of Data: While Google Analytics provides data, deriving actionable insights from this data and applying it to optimize websites or marketing strategies requires understanding and expertise.
Despite these challenges, Google Analytics becomes more manageable with practice and learning. Here are some tips to overcome the difficulties:
- Start with Basics: Focus on understanding fundamental metrics like sessions, users, pageviews, and traffic sources before delving into more complex features.
- Follow Tutorials and Guides: Google offers tutorials, documentation, and online courses through Google Analytics Academy, which can help in learning the tool step by step.
- Experiment and Explore: Play around with different reports, settings, and features within Google Analytics to get hands-on experience. Experimentation helps in understanding how changes impact data.
- Seek Help and Community Support: Online forums, communities, and resources often have valuable tips and solutions to common challenges users face while using Google Analytics.
- Take it Gradually: Don’t try to absorb everything at once. Break down the learning process into manageable chunks and gradually build on your knowledge.
With persistence and continuous learning, Google Analytics becomes less daunting, and users can harness its power to gain valuable insights into website performance and user behavior.
Can I learn Google Analytics on my own?
Absolutely, you can learn Google Analytics on your own! Google offers a range of resources and tools to help beginners understand and master the platform:
- Google Analytics Academy: It provides free online courses covering various aspects of Google Analytics. These courses include video lessons, quizzes, and practical exercises to help you learn at your own pace.
- Documentation and Help Center: Google’s official documentation and help center offer detailed guides, articles, and FAQs that cover almost every aspect of Google Analytics. It’s a valuable resource for understanding specific features and functionalities.
- Online Tutorials and Blogs: Numerous websites and blogs offer tutorials, tips, and how-to guides on using Google Analytics. They often break down complex concepts into simpler, actionable steps.
- YouTube and Video Tutorials: Video tutorials on platforms like YouTube provide visual guides to understanding Google Analytics. Many channels offer comprehensive guides for beginners.
- Practice and Experimentation: The best way to learn is by practicing. Set up a test or demo account and experiment with different features within Google Analytics. This hands-on experience helps reinforce your learning.
- Community Forums and Discussion Groups: Joining online forums, discussion groups, or communities related to Google Analytics allows you to ask questions, learn from others’ experiences, and stay updated on tips and best practices.
Remember, learning Google Analytics is a gradual process. Start with the basics, understand core metrics like sessions, users, and traffic sources, and gradually explore more advanced features as you become comfortable. It’s a tool that rewards continuous learning and experimentation, so don’t be afraid to dive in and explore!




