Gynecomastia Review
Gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of breast tissue in males, often caused by an imbalance of hormones. It can happen at any age and for various reasons, including hormonal changes, certain medications, obesity, or underlying health conditions.
Treatment options for gynecomastia depend on its underlying cause and severity. In some cases, lifestyle changes like weight loss or discontinuing certain medications may help reduce the condition. However, for persistent cases or those causing significant discomfort, surgical procedures such as liposuction or mastectomy might be recommended.
Reviews on gynecomastia treatment can vary based on individual experiences and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment method. Some people find relief and are satisfied with the results, while others may experience complications or have mixed feelings about the outcomes.
If you’re considering treatment for gynecomastia, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or a specialist who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation and needs. They can discuss the available options, potential risks, and expected outcomes to help you make an informed decision.
Is it good to have gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia itself is not inherently good or bad. It’s a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. Whether it’s considered “good” or not largely depends on the individual’s perspective and the impact it has on their life.
For some men, gynecomastia might not cause any significant physical discomfort or emotional distress. In such cases, it might not be a concern or seen as a problem.
However, for others, gynecomastia can lead to feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, or psychological distress. It may affect self-esteem, body image, and social interactions, causing emotional discomfort or impacting their quality of life.
The perception of gynecomastia often varies from person to person. Some individuals might embrace it as a natural aspect of their body, while others may seek medical intervention to address it, especially if it’s causing distress or discomfort.
Ultimately, whether gynecomastia is seen as “good” or not depends on how it affects an individual’s physical and emotional well-being and their personal feelings toward their body image.
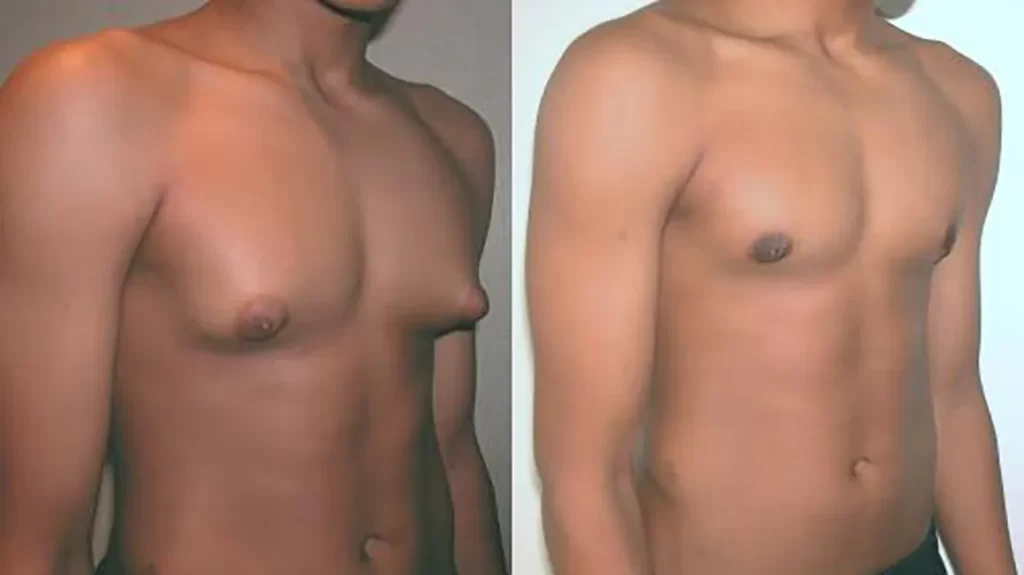
Is gyno surgery worth the money?
Deciding whether gynecomastia surgery (also known as gynecomastia correction or reduction surgery) is worth the money is a highly personal decision that depends on various factors:
- Impact on Quality of Life: For some individuals, gynecomastia causes significant emotional distress, affecting self-confidence, body image, and social interactions. In such cases, surgery might be considered a worthwhile investment to improve mental well-being.
- Severity of Gynecomastia: The degree of breast tissue enlargement and its impact on one’s physical appearance and comfort can influence the decision. For mild cases that don’t cause much distress, surgery might not be deemed necessary.
- Non-Surgical Options: Before opting for surgery, exploring non-surgical alternatives such as lifestyle changes (weight loss, discontinuation of medications that trigger gynecomastia) or hormonal treatments might be considered, especially for cases where surgery isn’t immediately necessary.
- Health Insurance Coverage: In some instances, health insurance might cover gynecomastia surgery if it’s considered medically necessary. Checking with insurance providers about coverage can influence the decision.
- Potential Risks and Expectations: Like any surgery, gynecomastia surgery carries risks such as infection, scarring, or asymmetry. Understanding these risks and having realistic expectations about the outcomes are crucial factors to consider.
Ultimately, whether gynecomastia surgery is worth the money varies from person to person. For some, the improvement in self-esteem and quality of life post-surgery may outweigh the costs and potential risks. Consulting with a qualified plastic surgeon or healthcare professional can provide tailored advice based on an individual’s specific case and preferences. They can discuss the available options, expected outcomes, and help in making an informed decision about whether surgery is the right choice.
Can gyno go away at 25?
Gynecomastia can resolve on its own in some cases, especially during puberty. However, if it persists beyond puberty and into adulthood, it’s less likely to resolve spontaneously. By the age of 25, gynecomastia that developed during puberty might have resolved for some individuals as their hormone levels stabilized.
Yet, if gynecomastia persists into adulthood, it’s less likely to spontaneously disappear. For some, hormonal changes, medications, weight loss, or lifestyle adjustments might help reduce the appearance of gynecomastia, but complete resolution might not occur without specific treatment.
If gynecomastia continues to be a concern into adulthood, consulting with a healthcare professional or a specialist is advisable. They can evaluate the underlying causes and suggest appropriate treatments, such as surgery or other interventions, based on individual circumstances.
Is gynecomastia shameful?
Gynecomastia, like any physical condition, shouldn’t be a source of shame. However, societal perceptions and personal feelings can impact how someone perceives their condition.
Feelings of shame often stem from societal stereotypes or unrealistic expectations regarding body image. Gynecomastia might challenge traditional notions of masculinity, leading some individuals to feel self-conscious or ashamed about their bodies.
It’s essential to understand that gynecomastia is a medical condition that many individuals experience. It’s not something to be ashamed of; rather, it’s a natural occurrence that can happen due to hormonal changes, medications, genetics, or other factors beyond one’s control.
Shame associated with gynecomastia often arises from societal pressures or personal insecurities. Addressing these feelings might involve seeking support from friends, family, or professionals who can offer understanding, empathy, and guidance. Open discussions and education about gynecomastia can also help reduce stigma and promote acceptance.
Ultimately, everyone’s journey with their body image and self-acceptance is unique. What matters most is how individuals perceive themselves and finding ways to feel comfortable and confident in their own skin, irrespective of any physical differences or conditions.
Is it OK to live with gynecomastia?
Absolutely, it’s okay to live with gynecomastia if it doesn’t cause physical discomfort or significant emotional distress. Gynecomastia is a common condition and, for many, doesn’t pose any health risks.
While some individuals might choose to seek treatment for gynecomastia due to psychological or emotional reasons, others might feel comfortable living with it without seeking intervention. If gynecomastia doesn’t negatively impact your quality of life, self-esteem, or cause discomfort, there’s no obligation to pursue treatment.
The decision to address gynecomastia through surgery or other interventions is highly personal. It’s essential to prioritize your comfort and well-being. If living with gynecomastia doesn’t affect your confidence, self-image, or health, it’s absolutely okay to embrace it as a natural aspect of your body.
Can gyno go away naturally?
In some cases, gynecomastia, particularly during puberty, might resolve naturally as hormone levels stabilize. During adolescence, hormonal imbalances can lead to temporary breast tissue enlargement in males, which often resolves on its own as hormone levels normalize.
However, once gynecomastia persists beyond puberty and into adulthood, it’s less likely to resolve spontaneously. Gynecomastia caused by factors like hormonal imbalances, certain medications, obesity, or underlying health conditions might not go away without specific interventions.
While some lifestyle changes, weight loss, or discontinuation of medications that trigger gynecomastia might help reduce its appearance, complete resolution might not occur without targeted treatment.
If gynecomastia is a concern and persists into adulthood, consulting with a healthcare professional or a specialist can provide guidance. They can evaluate the underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments, such as medication, hormone therapy, or surgery, based on individual circumstances.
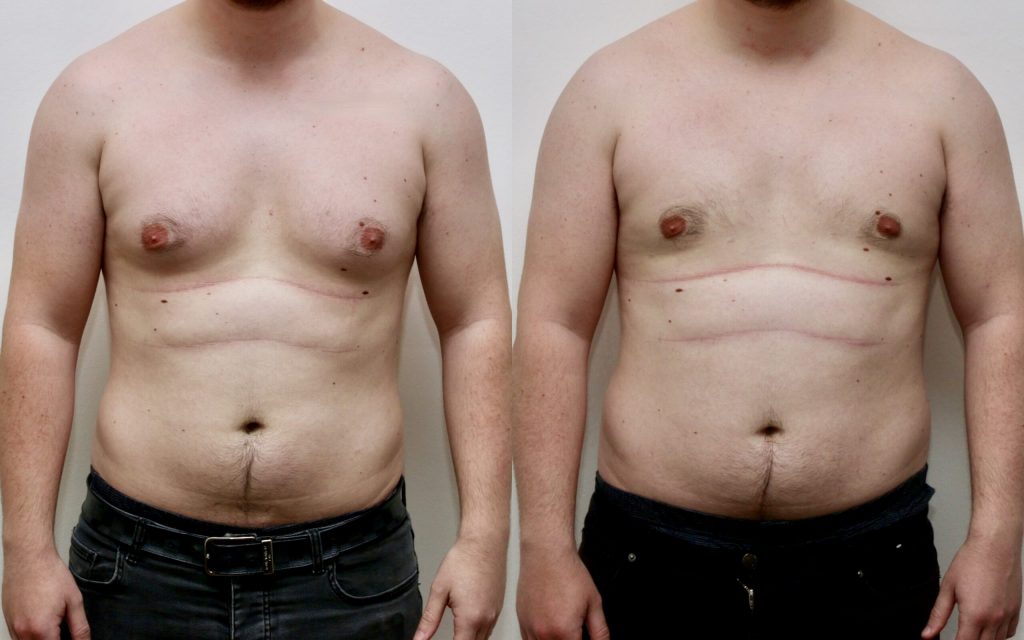
How painful is gyno surgery?
Gynecomastia surgery, like any surgical procedure, involves some level of discomfort or pain during the recovery period. However, the degree of pain experienced can vary among individuals and depends on several factors:
- Surgical Technique: The method used for gynecomastia surgery (such as liposuction, excision, or a combination) can impact the level of discomfort. More extensive procedures might result in a slightly longer and potentially more uncomfortable recovery.
- Individual Pain Tolerance: Each person’s pain tolerance varies, influencing how they perceive and manage post-operative discomfort.
- Medication and Pain Management: Surgeons often prescribe pain medications to manage discomfort during the recovery phase, which can significantly alleviate pain.
Typically, immediately after the surgery, there might be soreness, tenderness, and some degree of pain or discomfort in the chest area. This discomfort is often managed effectively with pain medications prescribed by the surgeon.
It’s essential to follow the surgeon’s post-operative care instructions diligently to minimize discomfort and promote healing. This may include wearing a compression garment, avoiding strenuous activities, and taking prescribed medications as directed.
Most individuals find that any discomfort experienced after gynecomastia surgery gradually lessens over a few days to a week. As the body heals, the discomfort diminishes, and the final results become more apparent.
Discussing any concerns about pain management with the surgeon before the procedure and adhering to the recommended post-operative care can help ensure a smoother recovery process.
Will gyno ever come back after surgery?
The recurrence of gynecomastia after surgery is rare but possible. Gynecomastia surgery aims to remove excess breast tissue and contour the chest for a more masculine appearance. However, there are scenarios where gynecomastia can potentially reoccur:
- Incomplete Removal: If the surgeon doesn’t completely remove all the glandular tissue or fat during the initial surgery, it might lead to a partial recurrence of gynecomastia.
- Weight Gain: Significant weight gain after surgery can result in the development of new fatty tissue in the chest area, mimicking the appearance of gynecomastia.
- Hormonal Changes: Subsequent hormonal imbalances or changes in hormone levels can occasionally stimulate the growth of breast tissue, leading to a recurrence.
To reduce the risk of gynecomastia recurrence after surgery, it’s essential to:
- Choose an experienced and qualified surgeon specializing in gynecomastia procedures to ensure thorough removal of excess tissue.
- Maintain a stable and healthy weight through proper diet and exercise to prevent the accumulation of additional fatty tissue.
- Follow post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon, including wearing compression garments and attending follow-up appointments.
Regular check-ups with the surgeon and maintaining overall health can help monitor any potential signs of gynecomastia recurrence and address them promptly if they arise.
Can gyno grow after surgery?
Gynecomastia recurrence after surgery, in terms of the regrowth of glandular breast tissue, is relatively uncommon. However, it’s crucial to understand that gynecomastia surgery doesn’t alter the body’s hormonal balance. Therefore, if there’s an underlying hormonal imbalance or a change in hormonal levels after surgery, there might be a possibility of new breast tissue growth.
Factors that can contribute to the growth of new breast tissue post-surgery include:
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels due to aging, certain medications, or underlying health conditions might stimulate the growth of breast tissue.
- Weight Gain: Significant weight gain after surgery can lead to the accumulation of fat in the chest area, resembling the appearance of gynecomastia.
- Incomplete Removal: If there’s residual breast tissue left behind during the initial surgery, it might contribute to potential regrowth.
To minimize the chances of gynecomastia recurrence or new growth after surgery, it’s essential to maintain a stable weight, follow a healthy lifestyle, and address any hormonal imbalances under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Regular follow-ups with the surgeon and monitoring any changes in the chest area can help detect and address any potential concerns early on.
Does gyno get worse over time?
The progression of gynecomastia can vary among individuals. For some, gynecomastia might stabilize or resolve on its own over time, especially if it’s related to hormonal changes during puberty. However, in other cases, gynecomastia can persist or worsen over time due to various factors:
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, which can occur due to aging, certain medications, or underlying health conditions, might contribute to the progression or persistence of gynecomastia.
- Weight Changes: Significant weight gain can lead to an increase in fatty tissue in the chest area, potentially worsening the appearance of gynecomastia.
- Underlying Causes: Gynecomastia caused by specific health conditions or medications might continue to progress if the underlying cause remains untreated.
- Lifestyle Factors: Factors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or the use of anabolic steroids can potentially exacerbate gynecomastia.
It’s important to note that while gynecomastia might remain stable or improve for some individuals, it can worsen for others, especially if underlying factors contribute to its progression. Monitoring any changes in the chest area, seeking medical advice, and addressing potential underlying causes are important steps in managing gynecomastia over time.
Can you lose gyno without surgery?
Yes, in some cases, gynecomastia can improve or resolve without the need for surgery. Here are some potential ways that gynecomastia might improve without surgical intervention:
- Lifestyle Changes: Engaging in regular exercise and following a healthy diet can help reduce overall body fat, potentially reducing the appearance of gynecomastia, especially if excess chest fat is contributing to the condition.
- Weight Loss: If gynecomastia is primarily due to excess body fat, losing weight through a combination of diet and exercise might lead to a reduction in breast tissue size.
- Discontinuation of Triggering Medications: If gynecomastia is caused by certain medications, stopping or changing these medications, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, may help improve the condition.
- Management of Underlying Health Conditions: Addressing underlying health issues or hormonal imbalances through appropriate medical treatment might lead to improvements in gynecomastia.
However, it’s important to note that while these approaches might help in some cases, they might not entirely resolve gynecomastia, especially if glandular breast tissue has developed. Surgical options like liposuction or glandular tissue excision might still be necessary for complete resolution, particularly for cases where the enlargement is primarily due to glandular tissue rather than fat.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or a specialist can help determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia and guide appropriate treatment options, whether surgical or non-surgical, based on individual circumstances.
Does gyno mean low testosterone?
Gynecomastia, the enlargement of breast tissue in males, can be associated with hormonal imbalances, including changes in testosterone and estrogen levels. However, it’s not always directly linked to low testosterone.
Gynecomastia can occur when there’s an imbalance between testosterone (male hormone) and estrogen (female hormone) levels. In some cases, a decrease in testosterone relative to estrogen or an increase in estrogen levels can contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
Several factors can lead to hormonal imbalances contributing to gynecomastia, such as:
- Puberty: During puberty, hormonal fluctuations can cause temporary gynecomastia as testosterone and estrogen levels change.
- Aging: As men age, testosterone levels might decrease while estrogen levels remain relatively stable, leading to an imbalance that can contribute to gynecomastia.
- Medications and Health Conditions: Certain medications, health conditions (such as liver or kidney disease), or hormonal disorders can influence hormone levels, potentially leading to gynecomastia.
However, it’s essential to note that not all cases of gynecomastia are directly linked to low testosterone. Some individuals with gynecomastia might have normal testosterone levels, while others might have a hormonal imbalance without low testosterone.
If gynecomastia is a concern, a healthcare professional or an endocrinologist can perform tests to evaluate hormone levels and identify any underlying hormonal imbalances contributing to the condition.
Can testosterone reduce gynecomastia?
Testosterone therapy isn’t typically used as a primary treatment for gynecomastia. While gynecomastia can occur due to an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen levels, the relationship between testosterone therapy and reducing gynecomastia is not straightforward and may not always be effective.
In some cases, if gynecomastia is associated with an imbalance where there’s relatively lower testosterone compared to estrogen, increasing testosterone levels might help rebalance hormones and potentially improve gynecomastia. However, the results can vary among individuals, and testosterone therapy might not be suitable or effective for everyone with gynecomastia.
It’s crucial to approach hormone therapy, including testosterone replacement therapy, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Testosterone therapy has potential side effects and risks, and its use should be carefully evaluated based on an individual’s overall health, hormone levels, and specific circumstances.
In cases where gynecomastia persists or causes significant distress, other treatment options such as surgery (liposuction, glandular tissue removal) or addressing underlying causes through lifestyle changes or medication might be more appropriate. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a specialist can provide personalized guidance on the most suitable treatment approach for gynecomastia.
How to reverse gynecomastia?
Reversing gynecomastia involves addressing its underlying causes or reducing the size of the enlarged breast tissue. Here are several approaches:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier lifestyle through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help reduce overall body fat, potentially minimizing the appearance of gynecomastia caused by excess fat tissue in the chest area.
- Weight Management: If excess weight contributes to gynecomastia, losing weight through a combination of diet and exercise can help reduce the size of the breasts.
- Medication Adjustment: If gynecomastia is a side effect of certain medications, consulting with a healthcare professional about potential alternative medications or dosage adjustments might help alleviate the condition.
- Addressing Hormonal Imbalances: Treating underlying hormonal imbalances, if present, might help reduce gynecomastia. This can involve medications or hormone therapy prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Surgery: In cases where gynecomastia doesn’t respond to non-surgical approaches or involves glandular tissue enlargement, surgical options like liposuction or glandular tissue excision may be necessary for complete reversal.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a specialist to determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia and identify the most appropriate treatment approach based on individual circumstances. They can provide tailored guidance and recommend the most effective options for reversing or managing gynecomastia.
What percent of men have gyno?
Estimates suggest that gynecomastia affects a significant percentage of men at some point in their lives. The prevalence of gynecomastia varies across different age groups and populations.
During infancy and adolescence, gynecomastia is relatively common. It affects around 60-90% of male newborns due to temporary hormonal changes from the mother. In adolescents, the prevalence ranges from 50-60%, mainly due to hormonal fluctuations during puberty.
In adult men, the prevalence is lower but still significant. Studies suggest that gynecomastia affects approximately 30-40% of adult males at some stage in their lives. This prevalence might be higher in specific populations or certain age groups due to factors such as hormonal changes, medication use, underlying health conditions, or lifestyle factors.
The prevalence rates can vary widely based on different studies, populations, and the criteria used to define and diagnose gynecomastia. Additionally, some cases of gynecomastia might go undiagnosed or unreported due to individuals not seeking medical attention for the condition.
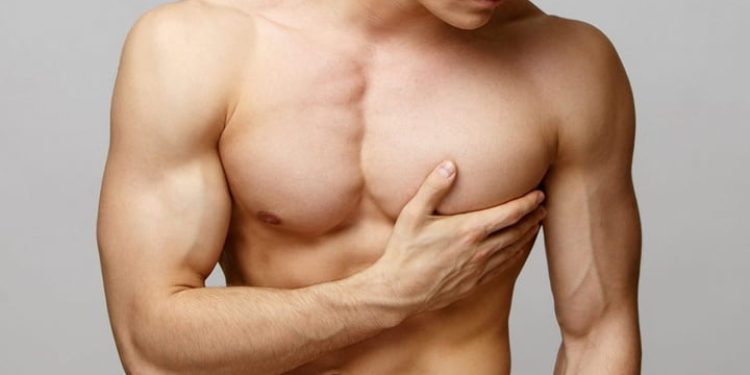
Can gym cure gynecomastia?
Exercise, particularly strength training and chest exercises, can help improve the chest’s appearance and reduce the prominence of gynecomastia to some extent, especially if excess fat contributes to the condition. Building chest muscles through targeted workouts might enhance the chest’s overall appearance and provide a more contoured look.
However, it’s important to note that while exercise can help tone the chest muscles and reduce overall body fat, it might not directly eliminate glandular breast tissue, which is often a significant component of gynecomastia.
If gynecomastia is primarily due to excess glandular tissue rather than fat, exercise alone might not fully reverse the condition. In such cases, surgical options like liposuction or glandular tissue removal might be more effective for achieving the desired reduction in breast tissue.
A comprehensive approach that includes exercise, a healthy diet, and targeted workouts can contribute to reducing the appearance of gynecomastia caused by excess fat. However, for cases involving glandular tissue enlargement, a consultation with a healthcare professional or a specialist is advisable to explore suitable treatment options tailored to individual circumstances.
Can vitamin D cause gynecomastia?
Vitamin D itself isn’t a known direct cause of gynecomastia. However, some studies have explored the potential link between vitamin D and hormonal balance, which indirectly might relate to gynecomastia.
Vitamin D plays a role in various bodily functions, including hormone regulation. Some research suggests that vitamin D might have an impact on testosterone levels. Testosterone imbalance, relative to estrogen, can contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
While there isn’t direct evidence establishing vitamin D as a direct cause of gynecomastia, hormonal imbalances influenced by factors like vitamin D levels can theoretically contribute to the condition. However, more research is needed to establish a clear connection between vitamin D and gynecomastia.
If you’re concerned about gynecomastia or vitamin D levels, consulting with a healthcare professional or an endocrinologist can provide personalized guidance and help determine if there’s any correlation between vitamin D levels and hormonal imbalances contributing to gynecomastia.
Does gyno hurt to touch?
Gynecomastia might be tender or sensitive to touch in some cases, especially if the breast tissue is swollen or enlarged. The degree of tenderness or pain can vary among individuals and might also depend on the underlying cause and the stage of gynecomastia.
In certain instances, gynecomastia can cause discomfort, tenderness, or sensitivity in the breast area, particularly if there’s inflammation or increased glandular tissue. This tenderness might be more noticeable when touching or applying pressure to the affected area.
However, not everyone with gynecomastia experiences pain or tenderness. In some cases, gynecomastia might not cause any discomfort and might be primarily a cosmetic concern.
If you’re experiencing pain, tenderness, or any changes in the breast area, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a specialist for proper evaluation and guidance. They can determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options based on your specific situation.
How long does gyno recovery take?
The recovery time after gynecomastia surgery can vary based on several factors, including the surgical technique used, individual healing abilities, and the extent of the procedure. Here’s a general timeline:
- Immediate Postoperative Period: Right after surgery, you might experience some discomfort, swelling, bruising, and soreness in the chest area. Pain medications prescribed by your surgeon can help manage this discomfort.
- First Week: During the first week, you’ll likely wear a compression garment to help reduce swelling and support the chest area. Strenuous activities should be avoided during this period.
- Two to Four Weeks: Most swelling and bruising tend to subside within a few weeks, but some residual swelling might persist for a few months. You may gradually resume light activities and work but should still avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting.
- Four to Six Weeks: By this time, many individuals can return to their normal activities, including more intense exercise, although it’s essential to follow the surgeon’s guidelines.
Full recovery from gynecomastia surgery can take several months, and the final results might not be fully apparent until the swelling completely subsides. The healing process can vary among individuals, so it’s crucial to follow your surgeon’s post-operative instructions diligently for optimal recovery.
Additionally, the specific instructions and recovery timeline can differ based on the surgical technique used, so it’s important to discuss expectations and recovery details with your surgeon before the procedure.
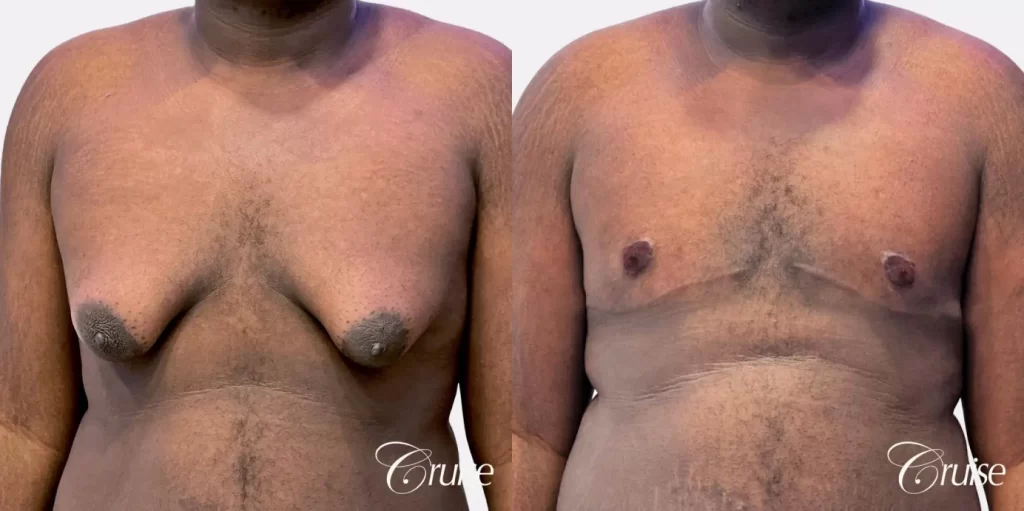
How long is gynecomastia recovery?
The recovery period after gynecomastia surgery can vary for each individual and depends on factors such as the surgical technique used, the extent of the procedure, and how well your body heals. Generally, here’s a breakdown of the recovery timeline:
- Immediate Postoperative Period (First Week): Right after surgery, there will likely be some discomfort, swelling, bruising, and soreness in the chest area. Pain medication prescribed by your surgeon can help manage this discomfort.
- First Few Weeks: During the initial weeks, you’ll typically wear a compression garment to support the chest area and minimize swelling. Strenuous activities, including heavy lifting and intense exercise, should be avoided during this time.
- Two to Four Weeks: Most swelling and bruising tend to decrease significantly within a few weeks, although some residual swelling might persist for a few months. You can gradually resume light activities and work, but follow your surgeon’s guidance on activity levels.
- Four to Six Weeks: By this time, many individuals can return to their normal routines, including more vigorous exercise, but it’s crucial to ease back into activities and avoid overexertion.
- Long-Term Healing: Full recovery from gynecomastia surgery can take several months. The final results might not be fully apparent until the swelling completely subsides, which could take a few months.
Remember, everyone heals at their own pace, so your specific recovery timeline might differ. It’s essential to follow your surgeon’s post-operative instructions diligently to optimize healing and achieve the best possible results. Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will also allow them to monitor your progress and provide guidance throughout the recovery process.
Are you awake during gyno surgery?
The type of anesthesia used during gynecomastia surgery depends on various factors, including the extent of the procedure and the surgeon’s preference. Generally, there are three main types of anesthesia used:
- Local Anesthesia with Sedation: In this case, the surgeon numbs the surgical area using a local anesthetic, and you’re given sedation to relax and potentially doze off during the procedure. You’re not fully unconscious but in a state of deep relaxation.
- General Anesthesia: With general anesthesia, you’re completely unconscious and unaware of the surgery. You’re not awake or conscious during the procedure.
- Twilight Anesthesia (IV Sedation): This anesthesia induces a state where you’re conscious but deeply sedated. You might have limited awareness or memory of the procedure.
The choice of anesthesia is typically discussed between you and your surgeon before the surgery, considering factors such as the complexity of the procedure, your medical history, and personal preferences.
The type of anesthesia used will determine whether you’re awake, partially awake, or completely unconscious during gynecomastia surgery. It’s essential to discuss any concerns or preferences regarding anesthesia with your surgeon beforehand to ensure your comfort and understanding of the procedure.
Why does my chest look weird after gyno surgery?
It’s normal for your chest to appear different or even “weird” immediately after gynecomastia surgery. Swelling, bruising, and changes in shape are common in the initial stages of recovery. Factors such as the surgical technique used, the body’s healing process, and individual differences contribute to how the chest looks post-surgery.
Swelling: Swelling is a natural part of the body’s healing process after surgery. It can distort the appearance of the chest temporarily, making it look uneven or unusual. As the swelling gradually subsides over time, the chest contour should improve.
Bruising: Bruising is also common after surgery and can contribute to the initial appearance of the chest. It usually resolves as the body heals.
Residual Tissue: Sometimes, the appearance might seem different due to residual breast tissue or asymmetry, which can take some time to settle and for the final results to become evident.
Healing Process: Each person’s healing process is unique, and the final results might not be immediately apparent. It can take weeks to months for the swelling to fully resolve and for the chest to take on its final appearance.
If you have concerns about how your chest looks after gynecomastia surgery, it’s essential to communicate with your surgeon. They can provide insight into what to expect during the recovery process and address any specific concerns you might have. Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will allow them to monitor your progress and ensure that the healing is proceeding as expected.
How do I shape my chest after gynecomastia surgery?
Shaping your chest after gynecomastia surgery involves a combination of factors, including post-operative care, exercise, and patience during the recovery process. Here are some steps that can help:
- Follow Post-Operative Instructions: Adhere to your surgeon’s instructions diligently. This includes wearing compression garments as directed, attending follow-up appointments, and following guidelines for activities and exercises.
- Allow for Healing: Give your body time to heal. The initial weeks after surgery are crucial for recovery. Avoid strenuous activities or exercises not approved by your surgeon during this period.
- Gradual Return to Exercise: Once your surgeon gives the green light, gradually reintroduce exercise into your routine. Focus on exercises that target the chest muscles, such as chest presses, push-ups, and chest flyes. However, it’s essential to start slowly and gradually increase intensity to avoid strain or injury.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet and regular exercise are essential for overall health and can contribute to shaping your chest after surgery. Maintain a healthy weight to optimize the results of the procedure.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly monitor your progress and discuss any concerns with your surgeon during follow-up appointments. They can provide guidance on exercises or adjustments tailored to your specific situation.
- Be Patient: Remember that the final results of gynecomastia surgery can take time to fully manifest. It might take several months for swelling to subside completely and for the chest to settle into its final shape.
Always consult with your surgeon before starting any exercise regimen post-surgery to ensure that you’re following the appropriate timeline and exercises that are safe and beneficial for your recovery. Each individual’s recovery process is unique, so it’s essential to have personalized guidance from your healthcare provider.
Can I do bodybuilding after gynecomastia surgery?
Yes, you can engage in bodybuilding and strength training after gynecomastia surgery, but it’s important to follow your surgeon’s guidelines and recommendations for exercise.
Once you’ve fully healed and received clearance from your surgeon, you can gradually resume strength training and bodybuilding exercises. It’s essential to start slowly and increase the intensity of your workouts gradually to avoid putting excessive strain on the chest area during the initial stages of recovery.
When engaging in bodybuilding or weightlifting exercises after gynecomastia surgery, consider the following:
- Gradual Progression: Start with lighter weights and low-intensity exercises, gradually increasing as your body adjusts and heals.
- Focus on Form: Pay attention to proper form and technique to prevent injury and avoid strain on the chest muscles.
- Avoid Overexertion: Listen to your body and avoid overexerting yourself, especially in the chest area, to prevent discomfort or potential complications during the healing process.
- Consult Your Surgeon: Always follow your surgeon’s recommendations regarding the timeline for resuming specific exercises and the level of intensity that’s safe for your recovery.
- Use Supportive Gear: Consider wearing appropriate supportive gear or compression garments during workouts, especially in the early stages of your return to bodybuilding.
Remember that each person’s recovery timeline and tolerance for exercise can vary, so it’s crucial to communicate with your surgeon and get personalized advice before engaging in intense physical activities like bodybuilding post-surgery.
Does testosterone increase after gynecomastia surgery?
Gynecomastia surgery itself doesn’t directly cause an increase in testosterone levels. However, in some cases, resolving gynecomastia might indirectly impact hormonal balance.
Gynecomastia is associated with an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen levels. The surgery aims to remove excess breast tissue and contour the chest, which can potentially alleviate the hormonal imbalance, especially if the gynecomastia was caused by an increase in estrogen relative to testosterone.
After successful gynecomastia surgery, some individuals might experience a more balanced hormonal state, where testosterone levels relatively increase or estrogen levels decrease compared to pre-surgery levels. However, this change isn’t a direct result of the surgery boosting testosterone but rather a correction of the hormonal imbalance associated with gynecomastia.
It’s important to note that the impact on hormone levels after gynecomastia surgery can vary among individuals, and surgery might not significantly affect hormone levels for everyone. Hormonal changes should be discussed with a healthcare professional, especially if there are specific concerns or underlying conditions affecting hormone balance.
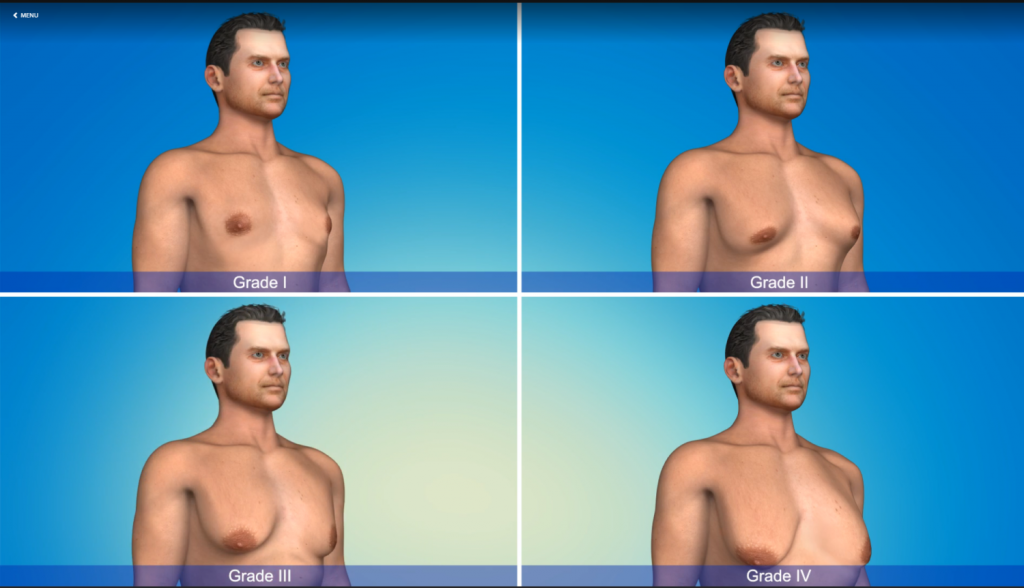
What is stage 2 gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is often categorized into different stages based on the severity and presentation of the condition. The classification into stages helps healthcare professionals determine the appropriate treatment approach. While classifications can vary slightly among sources, generally, gynecomastia stages are described as follows:
Stage 1: This stage typically involves a small amount of glandular tissue enlargement without excess skin. The chest might appear relatively flat, and the enlargement is not very noticeable under clothing.
Stage 2: In stage 2 gynecomastia, there is moderate glandular tissue enlargement with or without excess skin. The chest might have a more noticeable appearance of fullness or enlargement, which might be visible under clothing.
Stage 3: This stage involves significant glandular tissue enlargement with excess skin. The chest might have a visibly enlarged and sagging appearance, often noticeable both clothed and unclothed.
Stage 4: Stage 4 gynecomastia represents severe glandular tissue enlargement with significant excess skin. The chest might have a pendulous or hanging appearance, causing considerable physical and psychological discomfort.
Each stage represents a spectrum of gynecomastia severity, and the appropriate treatment options can vary depending on the stage. Less severe cases might respond well to non-surgical approaches like lifestyle changes or medications, while more advanced stages might require surgical intervention for optimal results.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or a specialist can help determine the stage of gynecomastia and guide the most suitable treatment options based on individual circumstances.
Can stress cause gyno?
Stress itself isn’t a direct cause of gynecomastia. However, stress can indirectly contribute to hormonal fluctuations, which might potentially influence the development of gynecomastia in some cases.
Gynecomastia is often linked to hormonal imbalances, specifically an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen levels. Stress can impact hormone levels by increasing the production of cortisol, the stress hormone, which, in turn, can influence the balance of other hormones in the body, including testosterone and estrogen.
Chronic stress might disrupt the endocrine system, affecting hormone levels and potentially contributing to imbalances that could lead to gynecomastia. However, it’s important to note that while stress might play a role in hormonal fluctuations, it’s not typically considered a primary or direct cause of gynecomastia.
Gynecomastia is more commonly associated with factors such as puberty, hormonal changes, certain medications, underlying health conditions, genetics, and lifestyle factors rather than stress alone.
If you’re experiencing concerns about gynecomastia or hormonal imbalances, consulting with a healthcare professional can help identify the underlying causes and provide appropriate guidance or treatment options.



